Globalization has transformed the way the world conducts business, and the art industry is no exception. The art market has experienced significant changes and challenges as a result of globalization, affecting not only the ways in which art is produced, distributed, and consumed but also the way it is valued and understood. Globalization has brought new opportunities, such as increased access to art and the growth of international art fairs, while also posing challenges, including the potential loss of cultural heritage and authenticity. Understanding the impact of globalization on the art business is crucial for artists, collectors, dealers, and other stakeholders who want to navigate the evolving landscape of the art world.
The Globalization of the Art Industry
The globalization of the art industry has led to significant changes in the way art is produced, distributed, and consumed. One of the most notable impacts of globalization has been the internationalization of art institutions. Major museums and galleries have expanded their presence in different parts of the world, creating new opportunities for artists and collectors. The globalization of art education has also enabled students to study and learn about art from different cultural perspectives, leading to the development of new artistic styles and themes.
However, increased competition is one of the challenges brought about by globalization. The rise of emerging markets has led to a shift in the balance of power in the art world, with new players entering the market and challenging the dominance of established markets such as Europe and North America. Cultural differences can also pose challenges for artists, dealers, and collectors who need to understand the specific cultural context of a work of art to appreciate its value and significance.
Globalization has also led to changing business models in the art world. The growth of art investment has transformed the way art is bought and sold, with investors viewing art as an alternative asset class that can provide returns on investment. This has led to a focus on the financial value of art, rather than its aesthetic or cultural value. Furthermore, the role of art as a commodity has increased, with some artworks being viewed primarily as investments rather than as works of art to be appreciated and enjoyed.
The Challenges and Opportunities of Globalization in the Art Business
The impact of globalization on the art business has brought with it both challenges and opportunities. One of the key challenges is cultural preservation and authenticity. As art becomes more globally distributed, it can be challenging to maintain cultural authenticity and prevent cultural appropriation. This challenge is particularly significant when dealing with works of art that have a deep cultural and historical significance.
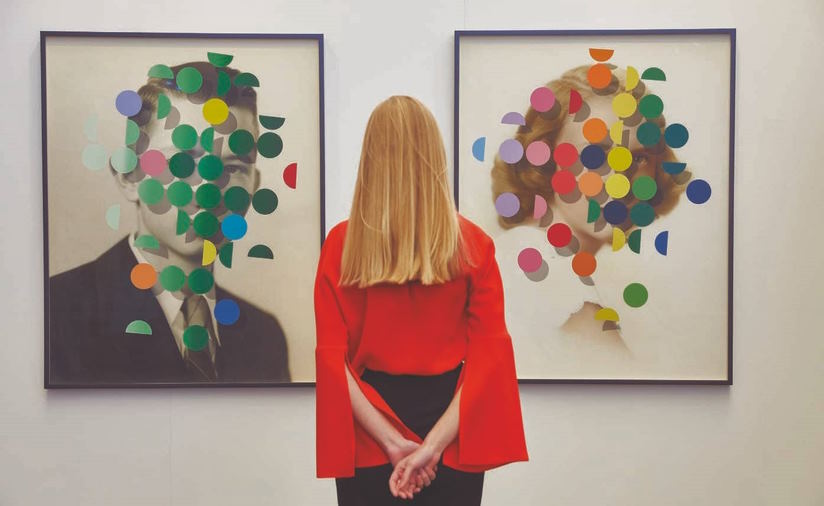

The globalization of the art industry can also have a significant impact on local art markets. As international markets grow, it can be difficult for local artists and dealers to compete, leading to a potential loss of cultural identity and heritage. It is essential to find ways to balance the benefits of global trade with the need to support and sustain local art markets.
The art industry is also facing pressure to become more sustainable and socially responsible. From reducing the environmental impact of art production to promoting diversity and inclusivity, the industry is being called upon to address important social and environmental issues. The rise of ethical and sustainable practices in the industry presents an opportunity for artists, collectors, and dealers to lead the way in creating a more responsible and sustainable industry.
Finally, the globalization of the art industry has created exciting opportunities for artistic collaboration and exchange. As artists and collectors from different parts of the world come together, new artistic styles and themes are emerging, creating a vibrant and diverse art world. This exchange of ideas and perspectives is essential for the growth and development of the industry.