Climate change has become one of the most pressing issues of our time, with its devastating effects being felt across the globe. Its impact can be seen in various fields, including art, where contemporary artists have responded to this crisis in various ways. In Europe, climate change has influenced the themes, materials, and techniques used by artists, creating a new wave of art that raises awareness about the issue and promotes sustainable practices. This article will explore the impact of climate change on contemporary European art, looking at how artists approach this theme, the use of sustainable materials, and the impact on the art market. By examining these aspects, we can gain a deeper understanding of the role of art in promoting environmental awareness and sustainable practices.
Climate change as a recurring theme in contemporary European art
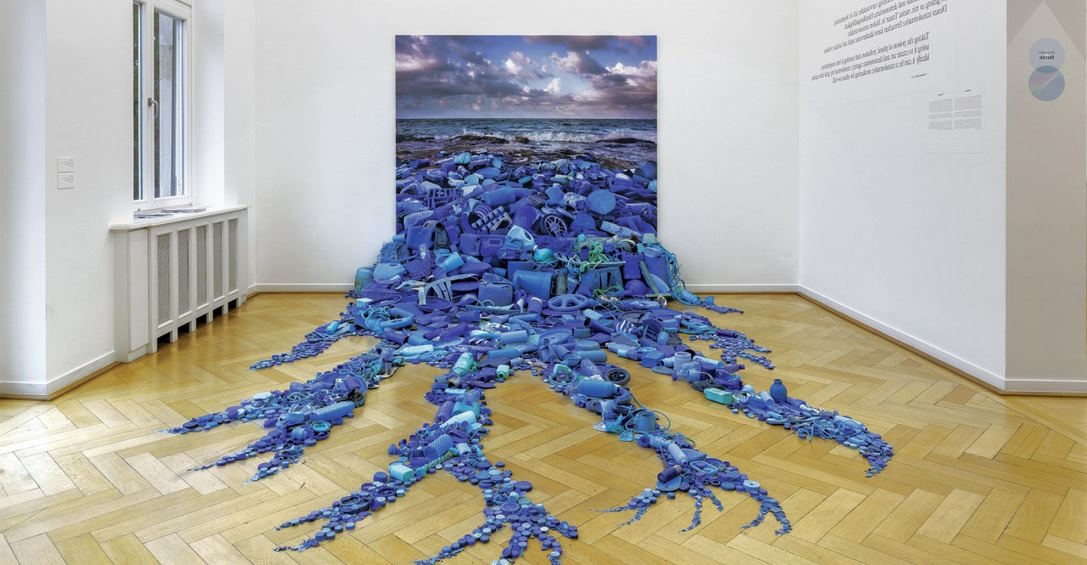
Climate change is a recurring theme in contemporary European art, with many artists using their work to raise awareness about the issue and highlight its devastating effects on the planet. One example of such artwork is Olafur Eliasson’s “Ice Watch,” which featured twelve massive ice blocks that were harvested from Greenland and placed in public spaces in cities around the world. The installation served as a visual representation of the melting ice caps and the urgency of the climate crisis.
Other artists, such as Jannis Kounellis, have used materials such as coal and soil to comment on the destructive impact of human activity on the environment. Kounellis’ “Untitled” (12 Horses) featured twelve live horses standing in a room filled with coal, highlighting the relationship between industrialization and environmental degradation.
The approach taken by European artists in addressing climate change themes varies, with some using a more direct and confrontational approach, while others opt for a more subtle approach. For instance, German artist Anselm Kiefer’s “Am Anfang” features a barren landscape, referencing the devastating effects of deforestation and habitat destruction.
Comparing the approach taken by European artists to those in other parts of the world, we can see differences in style and content. For instance, African artists such as El Anatsui and Romuald Hazoumè often incorporate found materials such as discarded plastic bags and jerry cans to highlight the environmental impact of consumer culture on their respective societies.
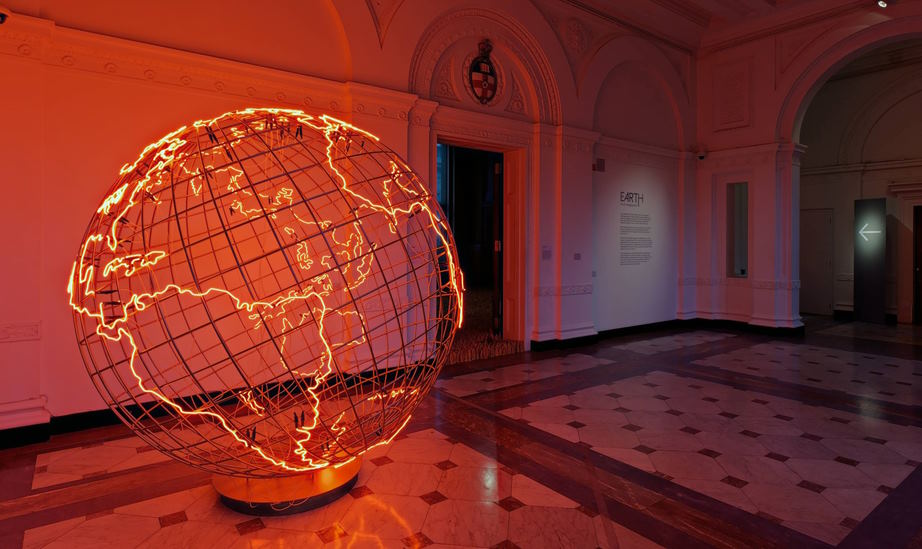

The use of sustainable and eco-friendly materials
As the impact of climate change becomes increasingly evident, artists have become more conscious of the environmental impact of their materials. Many contemporary European artists have embraced sustainable and eco-friendly materials, such as recycled materials or natural pigments, in their work. For instance, Danish-Icelandic artist Olafur Eliasson’s “Ice Watch” installation featured massive ice blocks harvested from Greenland, highlighting the urgent need for action on climate change.
Other artists, such as Michelangelo Pistoletto, have used recycled materials in their work to create environmentally conscious pieces. Pistoletto’s “Quadri specchianti” series features mirrors made from recycled materials that reflect the viewer and their surroundings, highlighting the interconnectedness of all things.
However, finding sustainable materials can be a challenge for artists, as they often have to balance their artistic vision with the need to minimize their environmental impact. Some artists have overcome this challenge by sourcing materials locally, such as Spanish artist Jaume Plensa, who uses reclaimed wood from the surrounding area in his sculptures.

The impact of climate change on the art market
Climate change has had a significant impact on the art market, with many collectors and institutions showing an increased interest in climate change-themed artworks. This growing interest has led to an increase in the value of these artworks, as they become more sought-after by collectors.
One example of this is the work of American artist Mark Dion, whose sculptures and installations often focus on environmental issues. Dion’s work has gained prominence in recent years, with his piece “The Library for the Birds of London” selling for $200,000 at a Christie’s auction in 2018.
Collectors and institutions approach climate change-themed artworks with a heightened sense of awareness and a greater understanding of their significance. For example, the Tate Modern in London recently acquired the work of artist Vivian Suter, whose paintings depict the effects of climate change on her home in Guatemala. The acquisition reflects the growing interest in climate change-themed art and its significance in contemporary culture.
Furthermore, the art market has also been affected by the increased demand for sustainable materials in artworks. This has led to a rise in the use of environmentally friendly materials and techniques, which are seen as more valuable by collectors.